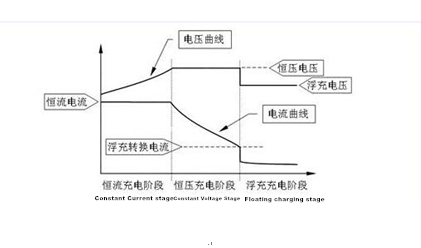
At present, the charger is mainly in three stages: constant current charging, constant voltage charging and floating charging, called three-stage charger. Starting charging with 2 amps, the voltage gradually increases, which called constant current charging; When the voltage reaches a certain value called constant voltage, For example the charger at about 40 volts, when reach to highest at 44 volts, this stage called constant voltage charging; The last stage, when the voltage reaches 44v, it begins to drop to the guaranteed point 41v, then starting trickle charging, charging slowly with the small current 200 ma. The last stage is mainly to guarantee that the battery is charging enough, and not overcharged at the same time, because the current is very small. If use two-stage charger or one-stage charger, it is easy to overcharge the battery.
The charging process for an ordinary three-stage lead acid battery charger as follows:
The charging process of a three-phase charger
-
During the constant current charging stage, the charging current of the charger remains constant, the charging power is increasing rapidly and the voltage of the battery rises.
-
During the constant voltage charging stage, the charging voltage of the charger remains constant, the charging power continues to increase, the voltage of the battery rises slowly, and the charging current drops.
-
The charging current drops below the floating charge current, and the charging voltage of the charger is reduced to the floating charge voltage.
-
During floating charging stage, charging voltage charger is keeping the same as the floating charging voltage.
 English
English  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  русский
русский  português
português  العربية
العربية  中文
中文